- Appointments :
- Book Online
- 99956 86614

Introduction: Lupus is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by the immune system mistakenly attacking healthy tissues and organs. It primarily affects women of childbearing age but can occur in individuals of any age or gender. The exact cause of lupus is unknown, but a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors is believed to play a role.
Symptoms:
Diagnosis: Diagnosing lupus can be challenging due to its varied presentation and similarity to other conditions. A combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and specific criteria established by the American College of Rheumatology are used for diagnosis. Blood tests measuring autoantibodies, such as antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and anti-double-stranded DNA (anti-dsDNA) antibodies, are commonly employed to support the diagnosis.
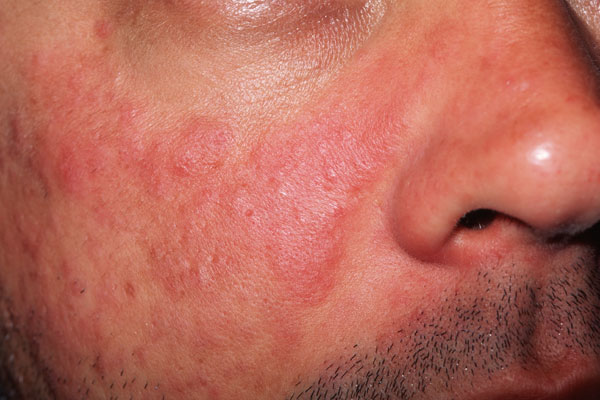
Treatment:
Conclusion: Lupus is a complex autoimmune disease that can affect multiple organs and systems in the body. Early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial for minimizing symptoms, preventing organ damage, and improving the overall well-being of individuals with lupus. Further research and ongoing advancements in treatment options offer hope for better outcomes and a brighter future for those living with this challenging condition.